Sea beetroot is the wild ancestor of beetroot, leaf beet and Swiss chard. It thrives along shores and estuaries, growing to a height of 1.2m (4 ft). The leaves are glossy with wavyedges and young ones make good eating. These can be picked in early spring. As with chard, these are best stripped off the ribs and then briefly steamed. The plant is adapted to grow in soils with a high concentration of salt but will also grow in rich, free-draining garden soils.

The sea breams are a large family of firm-fleshed fish which includes black sea bream, bogue, Couch’s sea bream (known as red porgy in North America), dentex, gilt-headed bream. They are usually sold weighing up to 1 kg (2 lb). All have a deep, narrow body, small mouth, big eyes, quite large, tough scales, a single, spiny dorsal fin and a black spot on the shoulder. They are good to eat cooked whole, stuffed and baked or braised.
The common sea buckthorn is widespread, growing from the Atlantic coasts of Europe and the UK right through the northwestern China. In western Europe, it is largely confined to coastal regions where salt spray off the sea prevents other larger plants from out-competing it, but in central Asia it is more widespread in dry semi-desert sites where other plants cannot survive the harsh conditions. The branches are dense and stiff and covered with thorns. This makes it difficult to harvest the orange berries which are only produced on the female plant. They are between 6–9 mm in diameter, soft, juicy and rich in oils.

Wolf-fish. Marine catfish. A fish of northern waters. It is medium oily and white-fleshed. Since it eats shellfish, its own flavour is good. Its jaws are strong and it has a blunt head which lend to its unattractive appearance, which is why it is normally sold filleted or in cutlets. It has few small bones and can be prepared in the same way as monkfish (US: angler fish), in stews or grilled. It is sometimes sold as rock salmon or rock turbot.
Surf clam. A large, ovoid clam, anything up to 15 cm (6 inches) across, with a yellowish-white shell with brown zig-zag markings, found in abundance in deep waters off the eastern coast of North America and South East Asia. This is most often cooked as one ingredient as part of a dish with many ingredients or in tinned, prepared dishes.
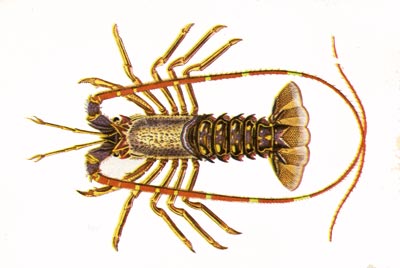
Crayfish. Spiny or rock lobster. Langouste. A salt water crustacean, not to be confused with freshwater crayfish.

Crayfish. Spiny or rock lobster. Langouste. A salt water crustacean, not to be confused with freshwater crayfish.

Trepang. An edible sea slug with tentacles at one end, treasured for its gelatinous texture in some parts of the world. It is usually available dried in the West, it should be soaked for 24 hours before use.

Monkfish (US: angler fish). A fish with a sweet flavour and succulent firm flesh but with the ugliest appearance imaginable. It is found in the Mediterranean and Atlantic, in coastal waters of north western Europe. It can be recognised by its large head and fan-shaped fins. The fins and the operculum are spiny. It can be eaten fried or in soup. The larger fish often have better flavour. It has a hideous head, which is why it is usually displayed without it, and a muddy colour. It is known as the anglerfish as it bears on its head a 'rod' and 'lure' which attract its prey. The meat of the tail is sweet and succulent - almost like lobster meat, entirely compensating for is appearance. The flavour may well be assisted by its own diet which is high in shellfish. The best monkfish are Lophius piscatorius and the similar Lophius budegassa, the favourite of the Spanish. American monkfish or goosefish (Lophius americanus) is considered inferior, while New Zealand monkfish (Kathetostoma giganteum) is related to the stargazer and is only fit for soup.